How Blood Clots Affect the Body
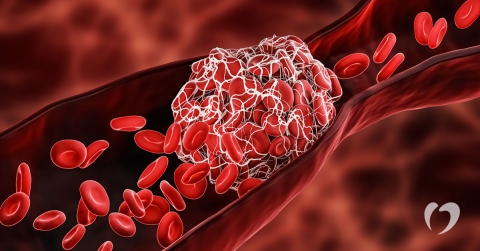
A blood clot is a collection of cells, protein, and platelets that have stuck to each other to form a semi-solid mass. Clotting is an important part of the body’s ability to heal. When there is an injury that causes bleeding, the body’s natural response is to stop the bleeding through clotting.
However, sometimes clots form inside veins due to an abnormal heart rhythm, inefficient blood flow, an injury to the area, or lack of movement. In these cases, clots stopping the flow of blood within the body can be dangerous.
Blood clots in extremities
When blood clots form in the arms or legs, symptoms can include pain, swelling, and discoloration of the skin. Clots in the arms can be caused by repetitive motion or repetitive injury to a particular spot. Clots in the legs are often a result of injury, infection, or poor circulation.
Blood clots in the brain or lungs
When clots form in or move to the brain or lungs, life-threatening conditions occur. While blood clots in the leg may not be life threatening initially, they can travel to the brain and cause a stroke due to reduced blood flow in the brain. Without quick treatment, a stroke can result in permanent damage or death.
When blood clots make their way to the lungs, pulmonary embolism occurs. Symptoms of a blood clot in the lungs can include shortness of breath, chest pain, faintness, and dizziness. Quick treatment of a pulmonary embolism increases the chances of survival.
Treatment for blood clots
Some blood clots naturally dissolve on their own over time. However, clots in the extremities that are large enough to cause pain, swelling, or skin discoloration require treatment. Many blood clots are treated with blood thinners that will prevent new clots from forming and allow the body time to dissolve the existing clot. If a clot is not dissolving on its own, there are other medication options to help dissolve the clot.
When blood clots threaten the lungs or brain, doctors may use a catheter procedure to remove the clot and prevent serious damage from occurring.
If you are experiencing symptoms of a blood clot, seek immediate medical attention. If you are concerned about a family history of heart conditions that can increase the risk of blood clots, such as atrial fibrillation, contact Oklahoma Heart Hospital to schedule an appointment with one of our physicians at the Heart Rhythm Institute.