What is an Electrocardiogram (ECG)?
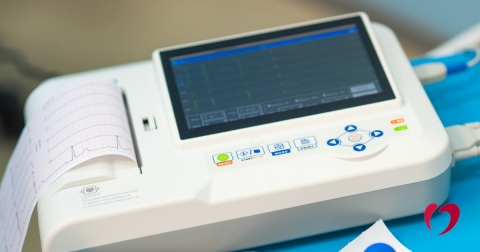
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a common tool used to diagnosis and assess heart conditions. It’s a road map of the electrical activity in the heart that a physician can follow to see what is or isn’t working properly. The ECG can present different patterns, but the more important use is identifying why a certain pattern has developed. At the Oklahoma Heart Hospital, ECGs are used to diagnose everything from heart attacks to a range of arrhythmias to thickening of the walls of the heart.
An ECG is a quick and painless in-office procedure that typically uses 12 leads (electrodes attached to sticky tabs) to assess the heart from multiple angles. The first six leads are placed on the arms and legs and the other six leads are placed on the chest in specific locations. The specific placement of the leads creates vectors that help provide a full measurement of what’s happening in the heart. If a patient is experiencing symptoms of a heart issue but has a normal in-office ECG, the patient may be sent home with a wearable heart monitor to capture additional data.
A good analogy for how an ECG works is to think of trying to describe a three-dimensional object to someone who has never seen that object. If you set that object in the middle of a table, you would need someone describing the object from each possible angle in order to get an accurate description. The specific locations of ECG leads provide that full view of what’s happening in the heart.
While the ECG is a quick procedure, it provides lots of information for assessing heart conditions. In addition to identifying rhythm issues, the ECG can also measure the size of each chamber of the heart and determine if the walls of the heart are thickening. For a patient with a premature ventricular contract (PVC) captured on an ECG, the test can help identify where in the heart the PVC originates within about a quarter-sized area. For patients with extra electrical pathways, an ECG helps determine what side of the heart contains the extra pathway and which direction the pathway travels in the heart. These details allow your physician to discuss treatment options and possible risks with you in order to determine the best course of action.
The ECG is an important diagnostic tool for use in emergency situations and when patients exhibit symptoms of possible heart problems, but its use as a pre-screening tool for athletes is increasing as well. Many states now require an ECG as part of pre-participation physicals for young athletes to screen for any underlying heart conditions that may cause sudden cardiac death if untreated. The use of ECGs is also common in international athletic competitions for athletes of all ages.
If you have questions about how electrocardiograms are used to diagnose heart conditions and inform treatment options, contact the Oklahoma Heart Hospital for more information.