Using Cardiac CT Scans to Diagnosis Heart Disease
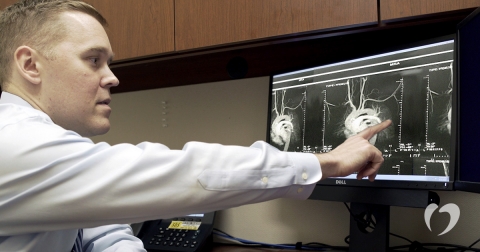
Computerized tomography (CT or CAT) scans can be used to evaluate health conditions in many parts of the body, including organs, tissue, and bones. A cardiac CT scan helps doctors view the structure of your heart and the surrounding arteries to diagnosis heart disease.
How does a CT scan work?
A CT scan uses x-ray to take pictures of your heart from different angles. Then a computer puts those pictures together to show a cross-sectional view of the heart. The test can be done with or without the use of contrast dye, depending on why the test is being done.
Types of cardiac CT scans
There are several types of cardiac CT scans that may be done depending on your symptoms and history of heart disease.
- Calcium score screening is used to determine if there’s a buildup of calcium in your heart. This test can provide early detection of atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries.
- Coronary CT angiogram (CTA) provides a three-dimensional view of the heart and the surrounding arteries that bring blood to your heart. This is a less invasive test than a traditional angiogram or cardiac catheterization, which involves inserting a catheter into the body to check the arteries.
Preparing for a cardiac CT scan
Cardiac CT scans are an outpatient procedure and most people are able to drive themselves home afterward. The day of your cardiac CT scan, you should avoid caffeine and smoking for at least four hours prior to the exam, and your doctor may ask you to avoid eating prior to the test as well.
What to expect during a cardiac CT scan
At the time of your scan, you’ll be asked to change into a gown and lie on a specialized table. You may be given medication to regulate your heartbeat during the exam. Several small, sticky discs called electrodes will be placed on your chest, and an IV will be inserted in your arm. If dye is being used, you may feel a warming sensation and may have a metallic taste in your mouth after the dye is administered.
You will be asked to lie in a specific position, and the radiology technician may use pillows or straps to help you hold that position. Once in position, the table will be moved into the CT machine where the x-rays are taken. Typically, the test lasts about 10 minutes, and you can continue with your usual day afterward. Drinking extra water will help flush the dye from your system.
After the completion of your cardiac CT scan, your doctor will review the results and discuss them with you at your next appointment.
If you have a family history of plaque or calcium in the arteries and want to assess your risk, contact the Oklahoma Heart Hospital today for an appointment with one of our physicians.